The global semiconductor industry has become a matter of national strategy, with countries racing to secure their position in the chip supply chain. The distribution of manufacturing capabilities across nations reveals critical dependencies, strategic advantages, and geopolitical vulnerabilities that shape the modern technology landscape.
The Top 10 Semiconductor Manufacturing Nations
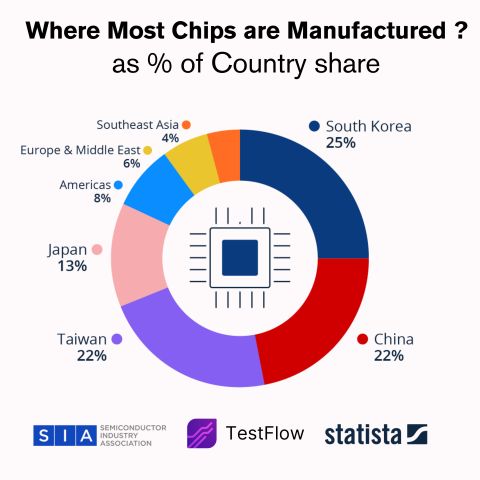
The global semiconductor manufacturing landscape is dominated by a select group of countries, each with distinct specializations and strategic advantages. Understanding this distribution is crucial for anyone working in the chip industry.
#1 Taiwan — ~19% Global Production
Advanced Node LeaderHome to TSMC, Taiwan dominates advanced-node manufacturing and produces the world's most sophisticated chips. From 3nm processors to AI accelerators, Taiwan is where cutting-edge silicon comes to life.
Key Strengths
- • TSMC's advanced node leadership
- • 3nm, 5nm manufacturing expertise
- • Advanced packaging capabilities
- • Complete semiconductor ecosystem
Major Products
- • Apple A-series processors
- • NVIDIA AI accelerators
- • AMD Ryzen and EPYC CPUs
- • Qualcomm Snapdragon SoCs
#2 South Korea — ~21% Global Production
Memory PowerhouseThe memory engine of the planet. Samsung and SK Hynix dominate global DRAM and NAND production, providing the memory infrastructure that powers everything from smartphones to data centers.
#3 China — ~21% Global Production
Rapid GrowthChina is rapidly scaling local fabs, foundries (like SMIC), and packaging capacity. Massive government investment aims to build a self-sufficient chip ecosystem, reducing dependence on foreign suppliers.
The Western Semiconductor Powers
While Asia dominates manufacturing volume, Western countries maintain critical roles in design, equipment, and specialized technologies:
| Country | Market Share | Primary Specialization | Key Companies |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | ~14% | Design, EDA tools, IP | Intel, NVIDIA, AMD, Qualcomm, Synopsys |
| Japan | ~9% | Materials, equipment, legacy nodes | Sony, Renesas, Tokyo Electron, Shin-Etsu |
| Europe | ~6% | Analog, automotive, equipment | ASML, Infineon, NXP, STMicroelectronics |
Specialized Regional Strengths: Beyond Manufacturing Volume
While production volume tells part of the story, each region has developed unique specializations that make them indispensable to the global semiconductor ecosystem:
United States: The Innovation Engine
While the US has lost manufacturing share, it remains the global leader in chip design, EDA tools, and intellectual property. American companies design the chips that the world manufactures.
Japan: The Materials Backbone
Japan dominates the materials and equipment that enable semiconductor manufacturing. From photoresists to etching gases, Japanese companies provide the chemical foundation of chip production.
The Asia-Pacific Manufacturing Hub
Asia-Pacific countries have become the manufacturing center of the global semiconductor industry, with each nation developing specific expertise and capabilities:
Singapore: Manufacturing Excellence Hub
A strategic manufacturing hub for companies like Micron and GlobalFoundries. Singapore is known for operational efficiency, reliability, and strong backend semiconductor capabilities.
Key Advantages
- • Strategic location for Asia-Pacific
- • Excellent infrastructure and logistics
- • Skilled technical workforce
- • Pro-business regulatory environment
Focus Areas
- • Memory manufacturing (Micron)
- • Foundry services (GlobalFoundries)
- • Backend assembly and test
- • Regional distribution hub
Malaysia: OSAT Powerhouse
Malaysia has emerged as a major player in outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) operations, hosting high-volume test and packaging centers for companies like ASE and Infineon.
Vietnam: Emerging Manufacturing Hub
An emerging location for backend operations, Vietnam is benefiting from supply chain diversification efforts and competitive labor costs, attracting investments from major semiconductor companies.
Israel: Innovation Concentrated
Despite its small size, Israel punches above its weight with Intel's advanced fabs and a thriving fabless startup ecosystem that drives innovation in specialized semiconductor applications.
Europe: The Equipment and Analog Specialist
European countries have carved out critical niches in semiconductor equipment, analog chips, and automotive semiconductors, maintaining strategic importance despite lower manufacturing volumes.
European Semiconductor Strengths
Netherlands: Equipment Leadership
ASML's monopoly on EUV lithography makes the Netherlands indispensable for advanced chip manufacturing worldwide. No EUV machines, no cutting-edge chips.
- • ASML: 100% EUV market share
- • Critical for 7nm and below
- • $200M+ per machine
- • Strategic export controls
Germany: Automotive Silicon
Infineon leads in automotive semiconductors and power management, critical for electric vehicles and industrial automation applications.
- • Infineon: Power semiconductors
- • Automotive focus (EVs, ADAS)
- • Industrial automation chips
- • Security and IoT solutions
Geopolitical Implications: The Strategic Semiconductor Map
The concentration of semiconductor manufacturing in specific regions creates both opportunities and vulnerabilities that have become central to national security considerations worldwide.
Strategic Vulnerabilities
- Taiwan Concentration: 90%+ of advanced chips from single region
- ASML Monopoly: Single point of failure for advanced manufacturing
- Supply Chain Risks: Natural disasters, geopolitical tensions
- Trade Dependencies: Export controls and trade restrictions
Diversification Efforts
- CHIPS Act: $52B US investment in domestic manufacturing
- European Chips Act: €43B to double EU production
- India PLI Scheme: Incentives for semiconductor manufacturing
- Foundry Expansion: TSMC fabs in US, Japan, Europe
"The chip race isn't just company vs company—it's country vs country. Semiconductors are now a matter of national strategy, with each nation doubling down on their unique strengths in the global supply chain."
The Validation Challenge: Supporting Global Manufacturing
As semiconductor manufacturing becomes more distributed across countries and regions, the validation and testing of chips becomes increasingly complex. Different regions may have different standards, requirements, and capabilities.

TestFlow: Global Validation Platform
Supporting semiconductor validation across all major manufacturing regions with unified, AI-powered testing capabilities
TestFlow's Global Support Strategy
Multi-Regional Compliance
TestFlow automatically adapts to different regional standards and requirements, ensuring chips validated on our platform meet specifications across all target markets.
Distributed Team Collaboration
Cloud-native architecture enables seamless collaboration between validation teams across different countries and time zones, accelerating global development cycles.
Supply Chain Resilience
AI-powered analytics help identify potential supply chain risks and optimize validation strategies to maintain continuity across different manufacturing regions.
Country-Specific Semiconductor Ecosystems
Each major semiconductor manufacturing country has developed unique ecosystem characteristics that reflect their strategic priorities and competitive advantages:
| Country | Ecosystem Focus | Government Strategy | Investment Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taiwan | Advanced manufacturing excellence | Technology leadership focus | High (R&D + infrastructure) |
| South Korea | Memory + foundry competition | Chaebol-driven innovation | Very High (Samsung, SK) |
| China | Self-sufficiency building | National semiconductor strategy | Massive (state-directed) |
| United States | Design + domestic manufacturing | CHIPS Act implementation | High (federal + private) |
| Japan | Materials + equipment leadership | Technology sovereignty | Moderate (targeted) |
The Future of Global Semiconductor Manufacturing
The global semiconductor manufacturing map is rapidly evolving as countries implement strategies to secure their positions in the chip supply chain. Several key trends will shape the future distribution:
Geographic Diversification
Companies are establishing manufacturing capabilities across multiple regions to reduce concentration risk and improve supply chain resilience.
- • TSMC expanding to US, Japan, Europe
- • Intel building fabs in multiple countries
- • Samsung establishing global presence
- • Memory companies diversifying locations
Specialized Ecosystems
Countries are focusing on their unique strengths rather than trying to replicate the entire semiconductor value chain domestically.
- • Design hubs (US, UK, Israel)
- • Manufacturing centers (Taiwan, Korea)
- • Materials suppliers (Japan, Europe)
- • Assembly and test (Southeast Asia)
Investment Trends: National Semiconductor Strategies
Governments worldwide are implementing massive investment programs to secure their semiconductor capabilities and reduce dependencies on foreign suppliers:
Major Government Investment Programs
Implications for Semiconductor Validation
The global distribution of semiconductor manufacturing creates unique challenges and opportunities for validation teams working across multiple regions and standards:
Multi-Regional Standards
Chips must meet different regulatory and technical standards across regions, requiring validation approaches that can handle diverse requirements simultaneously.
Distributed Teams
Validation teams often span multiple countries, requiring collaboration tools and methodologies that work effectively across time zones and cultures.
Supply Chain Resilience
Validation processes must account for potential supply chain disruptions and ensure chips can be manufactured reliably across different facilities and regions.
"The future of semiconductors won't be won in a single fab—but in a global supply chain. Every country is playing a different role, and the smartest ones are doubling down on their strengths."
Conclusion: The Interconnected Semiconductor World
The global semiconductor manufacturing landscape reveals an industry that is simultaneously concentrated and distributed, with each major region playing critical, specialized roles. Taiwan's advanced manufacturing, Korea's memory leadership, China's rapid scaling, America's design excellence, Japan's materials mastery, and Europe's equipment and analog expertise combine to create the global chip ecosystem.
As geopolitical tensions rise and countries seek greater semiconductor independence, the industry is entering a period of significant transformation. However, the technical complexity and massive capital requirements of modern chip manufacturing suggest that global collaboration will remain essential, even as countries build more domestic capabilities.
For companies working in this global ecosystem, understanding these regional dynamics is crucial for strategic planning, risk management, and operational success. The future belongs to organizations that can navigate this complex landscape while delivering the reliable, high-performance semiconductors that power our digital world.
Navigate Global Semiconductor Validation
Whether you're manufacturing in Taiwan, designing in the US, or testing across multiple regions, TestFlow provides the unified validation platform you need to succeed in the global semiconductor ecosystem. Our AI-powered approach adapts to regional requirements while maintaining consistent quality standards.